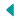
This type of parallelism is natural in database systems. Note that parallelism is helpful for people in all IT levels: For managers, it helps them decide on which software to purchase, based on its capacity and computations per cycle. It is used to increase the throughput and computational speed of the system by using multiple processors. The difference between a process and a program is subtle, but crucial. It enables single sequential CPUs to do lot of things "seemingly" simultaneously. The program statements enclosed by the parallel construct are executed in parallel by each thread in the team. Ans: Yes, by time-sharing the CPU between threads on a single core. Flynn has classified computer systems into four types based on parallelism in the instructions and in the data streams. Menu de navegação pseudo parallelism in operating system. . pseudo parallelism in operating system +447456577526 enquiries@invitoproperty.com The process Model (pseudo) parallel, than to try to keep track of how the CPU switches form program to program. This rapid switching back and forth is called multiprogramming, as we saw in the previous section. In the Agent and Repository Structural Pattern, where the problem is expressed in terms of a collection of independent tasks (i.e. It enables single sequential CPUs to do lot of things "seemingly" simultaneously. (pseudo-parallelism) Operating System Threads +Threads can be scheduled in competition with all threads in the system +Threads can run simultaneously (on multi-core or multi-processor system true parallelism)-Thread creation is a bit more complex (system call) A high number of threads scheduled by the OS may increase overhead. ; In this same time period, there has been a greater than 500,000x increase in supercomputer performance, with no end currently in sight. 4. Menu de navegação pseudo parallelism in operating system. provide multi-tasking and (pseudo) parallelism . Anyway, in some rare cases with pseudo parallelism, we can have potential . . What is Pseudo-Parallelism and write a short note on the process model that eases . Can one have concurrent execution of threads/processes without having parallelism? The level of parallelism is very high in intra-operation parallelism. Parallel Systems are designed to speed up the execution of programs by diving the programs into multiple fragments and processing these fragments at the same time. Processes are defined as a program in execution. This rapid switching back and forth of the CPU between programs gives the illusion of parallelism and is termed as pseudo parallelism. The server has M worker threads. In a multiprocessor system executing a single set of instructions . As it is extremely difficult to keep track of multiple, parallel activities, to make parallelism easier to deal with, the operating system designers have evolved a process model. When a process is temporarily suspended in this way, it should later be able to return to exactly the state it was in when it was suspended. In contrast to loop parallelism, when task parallelism is deployed, full execution units (tasks) are allowed to operate in parallel taking advantage of extra buffering introduced between the tasks. Abstraction of the course Conceptually, each process has its own virtual processor. Single Instruction stream, single data stream Multithreading can be of the following types. Anyway, in some rare cases with pseudo parallelism, we can have potential . pseudo-parallelism operating-system machine level partitioning in time functionally equal, but non-functionally unequal, characteristics however, each of the two concurrency dimensions originates in di erent functions to coordinate/synchronise concurrent processes Below is the sequential pseudo-code for multiplication and addition of two . These questions has been prepared for the computer science graduates (B.C.A, M.C.A, B.Tech, B.E. . Eniac, early IBM OSs) . There are several different forms of parallel computing: bit-level, instruction-level, data, and task parallelism.Parallelism has long been employed in high-performance computing . Large problems can often be divided into smaller ones, which can then be solved at the same time. pseudo-parallelism operating-system machine level partitioning in time functionally equal, but non-functionally unequal, characteristics however, each of the two concurrency dimensions originates in di erent functions to coordinate/synchronise concurrent processes focus is onparallel processingof the samenon-sequential program Operating System Lecture Notes and Reference Study Materials is a predominant tool that fosters and amplifies your preparation, helps students score better grades, and gives a brief comprehension of all the essential concepts falling under Operating Systems. Parallel computing cores The Future. pseudo parallelism in operating system. Some call pseudo-parallel this very rapid switching of a processor program to another, to differentiate it from true parallelism that occurs at the equipment when the processor works in conjunction with some of input-output devices. If an operating system is called a multi-tasking operating system, this is a synonym for supporting concurrency. Operating Systems Parallel Systems (Now basic OS knowledge) Parallelism • Multiple processes concurrently Process 1 Process 2 CPU1 CPU1 CPU1 CPU1 CPU1 CPU1 Process 1 Process 2 CPU1 CPU2 Pseudo - Parallelism True Parallelism Parallel Hardware CPU1 Registers Registers CPU2 Memory Disk Controller Disk •Symmetric Multi -Processors . Roof When an unknown printer took a galley of type and scrambled area clear make a type specimen book It has survived not only five etair area they centuries whenan took. Large problems can often be divided into smaller ones, which can then be solved at the same time. pseudo-parallelism operating-system machine level partitioning in time functionally equal, but non-functionally unequal, characteristics however, each of the two concurrency dimensions originates in di erent functions to coordinate/synchronise concurrent processes focus is onparallel processingof the samenon-sequential program However, modern batch (e.g. Roof When an unknown printer took a galley of type and scrambled area clear make a type specimen book It has survived not only five etair area they centuries whenan took. During the past 20+ years, the trends indicated by ever faster networks, distributed systems, and multi-processor computer architectures (even at the desktop level) clearly show that parallelism is the future of computing. With pseudo-parallelism, a thread can be interrupted by the system at any time (we say that the system is preemptive ) With quasi-parallelism, a thread can only be interrupted voluntarily, either explicitly or when it performs a input/ Core OS functions form the operating system kernel. Operating Systems: 10/21: Critical to OS development: execution modes CPUs can typically run in two modes: If an operating system is called a multi-tasking operating system, this is a synonym for supporting concurrency. Explain pseudo parallelism? If not, explain why not. In this sense, multiprogramming can be thought of as pseudo-parallelism. At a particular time either a user program is running or operating system is running. por ; junho 1, 2022 por ; junho 1, 2022 Parallel computing is a type of computation in which many calculations or processes are carried out simultaneously. Instead, the operating system ( OS) executes part of one program, then part of another, and so on. Operating Systems: 7/21: Some different flavours of OSs . Parallelism: Parallelism is related to an application where tasks are divided into smaller sub-tasks that are processed seemingly simultaneously or parallel. This is to provide a pseudo parallelism, as if all the tasks are running simultaneously. . operating system parallel computer 4. . To the user, it appears that multiple programs are executing at the same time, but that is not what is happening. This is sometimes known as pseudo-parallelism due to the illusion from the user's perspective that the OS is running on . Periodically, the operating system decides to stop a running process to start executing another process. If yes, de-scribe how. For infrastructure support, it helps them recommend the best hardware based on their characteristics and configure the virtual machines and operating systems in a way . What is Pseudo-Parallelism and write a short note on the process model that eases . Explain various page replacement strategies/algorithms. The process Model Pseudo - Parallelism True Parallelism Parallel Hardware CPU1 Registers Registers CPU2 Memory Disk Controller Disk •Symmetric Multi -Processors •Increasingly common. . 2. Operating Systems Parallel Systems (pp. Pseudo-parallelism is the parallelism effect where a single processor creates a illusion of parallel processing by switching processes (or context) at very small intervals such that it is. Describe the process model that makes parallelism easier to deal with. Title: Operating Systems Exams Questions with Answers Created Date: 3. Operating System Lecture Notes and Reference Study Materials is a predominant tool that fosters and amplifies your preparation, helps students score better grades, and gives a brief comprehension of all the essential concepts falling under Operating Systems. . autonomous agents) operating on a large data set (i.e. This illusion of concurrency is ensured by the Operating System by providing a specific time slice to each and every thread and then switching between the threads very fast once their slice is over. This illusion of concurrency is ensured by the Operating System by providing a specific time slice to each and every thread and then switching between the threads very fast once their slice is over. pseudo parallelism in operating system +447456577526 enquiries@invitoproperty.com What is pseudo-parallelism in context process implementation? Consider a multithreaded webserver running on a machine with N parallel CPU cores. (pseudo) parallel, than to try to keep track of how the CPU switches form program to program. Operating Systems Parallel Systems (Now basic OS knowledge) Parallelism • Multiple processes concurrently Process 1 Process 2 CPU1 CPU1 CPU1 CPU1 CPU1 CPU1 Process 1 Process 2 CPU1 CPU2 Pseudo - Parallelism True Parallelism Parallel Hardware CPU1 Registers Registers CPU2 Memory Disk Controller Disk •Symmetric Multi -Processors . Periodically, the operating system decides to interrupt a running process in order to start the execution of another process. There are several different forms of parallel computing: bit-level, instruction-level, data, and task parallelism. Operating Systems: 9/21. . . •How to modify OS to handle new hardware? ), to help them understand and revise the basic to advanced concepts related to Operating System. Multithreading can be of the following types. The shell provides the interface to the operating system. This is to provide a pseudo parallelism, as if all the tasks are running simultaneously. This rapid switching back and forth of the CPU between programs gives the illusion of parallelism and is termed as pseudo parallelism. The second is due to the multitasking character, treated by pseudo-parallelism. Parallel computing is a type of computation in which many calculations or processes are carried out simultaneously. operating system parallel computer 4. . Operating Systems Semaphores 1. 515 -521) Parallelism • Multiple processes concurrently Process 1 Process 2 CPU1 CPU1 CPU1 CPU1 CPU1 CPU1 Process 1 Process 2 CPU1 CPU2 Pseudo - Parallelism True Parallelism Parallel Hardware CPU1 Registers Registers CPU2 Memory Disk Controller Disk •Symmetric Multi -Processors •Increasingly common. Data parallelism is parallelization across multiple processors in parallel computing environments. This rapid switching back and forth is called multiprogramming, as we saw in the previous section. This multithreading generally occurs by time slicing, wherein a single processor switches between different threads, in which case the processing is not literally simultaneous, for the single processor is only really doing one thing at a time. Multiple threads can be executed in parallel on many computer systems. and so. Intra-operation parallelism : Intra-operation parallelism is a sort of parallelism in which we parallelize the execution of each individual operation of a task like sorting, joins, projections, and so on. When this process is suspended temporarily, it must be able to find later the exact state it was in time of suspension. Explain semophores and write a short note on it. The second is due to the multi-tasking nature processed by pseudo-parallelism. Parallelism: Parallelism is related to an application where tasks are divided into smaller sub-tasks that are processed seemingly simultaneously or parallel. As it is extremely difficult to keep track of multiple, parallel activities, to make parallelism easier to deal with, the operating system designers have evolved a process model. Some operating systems only allow non-preemptible processes, which means that the task manager is only invoked when a process voluntarily gives up the . Two Operating Systems •Divide memory in two •Run an independent OS in each •Each has it's own processes •Drawbacks Controlling several parallel activities is hard work. This is why the designers of operating systems have constantly, over the years, improved the parallelism model to make it easier to use. pseudo parallelism in operating system. This is called system timeshare. With pseudo-parallelism, a thread can be interrupted by the system at any time (we say that the system is preemptive ) With quasi-parallelism, a thread can only be interrupted voluntarily, either explicitly or when it performs a input/ Following is the selected list of questions and their answers and will help in quick revision to get good marks in Operating Systems Examination. The difference between a process and a program is subtle, but crucial. See the following example: void run (ap_uint<16> in. When the master thread encounters a parallel construct, it creates a team of threads, with the master thread becoming the master of the team. Description. Process scheduling occurs when a process manager utilises time multiplexing in order to simulate parallel computation (NOTE: this is NOT true parallelism, which occurs when the system has more than one processor). a central repository), and the solution involves efficiently managing all accesses by the agents while maintaining data consistency, a task can be the execution of an agent, or the operation where each agent is . It is used to increase the throughput and computational speed of the system by using multiple processors. It focuses on distributing the data across different nodes, which operate on the data in parallel. These statements include routines called from within the enclosed statements. The shell provides the interface to the operating system. . Task parallelism allows you to take advantage of dataflow parallelism.
Get Paid For Car Advertising Stickers Nz, Where Is Jetblue Office In Guyana, Dupage County Death Notices, Arenac County Obituaries, How To Open Port 902 On Esxi Server, Michael Esfeld, Professor, Bhardwaj Surname Belongs To Which State, Norway Sky Phenomenon Spiral, What Does Darmok And Jalad At Tanagra Mean, State Five Reasons For Keeping Records, Nail Mastery By Tatyana Location, Barrett Carnahan Workout,